Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
Sensors power Advanced Driver Assistance Systems to keep you
safe on the road.
Sensors are an integral part of Advanced Driver Assistance
Systems (ADAS). By using sensors such as radar and cameras to perceive the
environment around it, ADAS can provide both warnings and take automatic action
to keep drivers safe on the road. Through the implementation of these safety
features, ADAS is able to alert drivers to potential hazards or even intervene
to avoid a collision altogether. In this blog post, we'll explore how sensors
power Advanced Driver Assistance Systems to keep you safe on the road.
What are Advanced Driver Assistance Systems?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are a set of
safety features found in newer vehicles that help the driver navigate more
safely on the road. ADAS helps drivers by using sensors to detect the environment
around the vehicle, such as other cars, pedestrians, animals, and road
obstacles. The system then provides the driver with information or can even
take action to prevent accidents from occurring. Examples of ADAS features
include forward collision warning systems, blind spot monitoring, lane
departure warning, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control. By
utilizing these advanced safety features, ADAS provides drivers with an added
layer of protection when driving.
How do sensors power ADAS?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) use sensors to
sense the environment around the vehicle and then take automatic action.
Sensors detect objects in the vehicle’s path and provide information to the
driver or take action on their own. Radar, cameras, and other sensors are used
to perceive the environment and provide warnings, lane departure warnings,
blind spot detection, and other features. The system works by combining data
from multiple sensors to create a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s
surroundings.
For example, radar is often used for long-range sensing,
while cameras are better at detecting close-up objects. By using data from both
sensors, the ADAS can accurately predict obstacles in the vehicle’s path and
respond accordingly.
The Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) feature is an example
of how ADAS uses sensors to automatically react to a potential collision. If a
sensor detects an obstacle ahead, it will warn the driver and, if necessary,
take automatic action such as applying the brakes. This can help reduce the
risk of a collision and reduce the severity of any resulting damage.
ADAS also uses sensors to provide convenience features such
as lane-keeping assist or adaptive cruise control. These features use sensors
to detect lane markings on the road and maintain a safe distance from other
vehicles. This makes driving more comfortable and can help reduce fatigue on
long trips.
Overall, sensors are an integral part of the ADAS system,
providing critical information about the vehicle’s surroundings and enabling it
to take automated action when necessary.
What are some of the most common ADAS features?
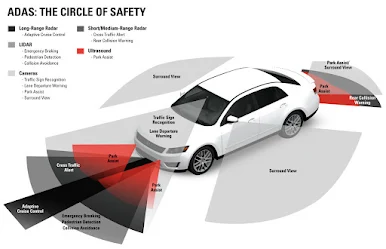
ADAS features |
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are safety
features that are becoming more and more common in vehicles today. These systems
use sensors to monitor the surrounding environment and provide drivers with
information or take automatic action, depending on what is perceived. Some of
the most common ADAS features include:
• Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): This feature uses sensors
to detect the speed and distance of the vehicles around it and then adjust the
speed accordingly.
• Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB): Sensors detect
potential collisions with other vehicles and then automatically apply the
brakes to reduce the risk of an accident.
• Lane Departure Warning (LDW): LDW uses sensors to detect
when a vehicle is drifting out of its lane, and then provides a warning to the
driver.
• Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): Sensors detect objects in the
blind spot areas around the vehicle and then provide a warning if there is an
object that can’t be seen by the driver.
These features are designed to provide drivers with a
greater level of safety and awareness when on the road, and can help to reduce
the risk of accidents. It’s important to ensure that your vehicle’s ADAS system
is working properly, as many of these features rely on accurate sensors to
function correctly.
How can I make sure my ADAS is working properly?
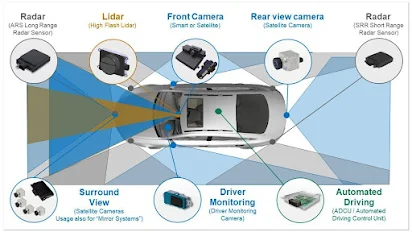
ADAS Working |
Maintaining an Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) is
essential for ensuring its proper functioning and safety on the road. Automatic
functions provided by ADAS are based on the information collected from sensors
located in the vehicle. To guarantee that the system is working properly,
regular inspections of the sensors should be conducted.
To check the functioning of your ADAS, look for any warning
signs that may appear when you start your car, or if you notice a decrease in
performance or accuracy of the features. It is also important to regularly
inspect the sensors for dirt, dust, or any physical damage that could affect
the performance of the system. If any faults are found with the sensors, they
should be replaced as soon as possible.
Lastly, ensure that all the components connected to the
system are properly calibrated and updated. It is recommended to have a
professional inspect your ADAS at least once a year to ensure its optimum
performance and keep you safe on the road.
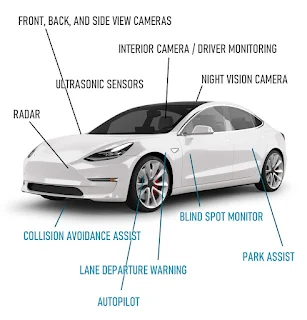
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Sensors
At the heart of every Advanced Driver Assistance System
(ADAS) are sensors. These sensors are placed throughout a vehicle, monitoring
and assessing the surrounding environment. They use data such as speed,
distance and angles to provide the vehicle’s driver with information and can
even take automatic action based on what they perceive.
The most common types of ADAS sensors include
- · Cameras
- · Radars
- · Lasers
Cameras are used to detect nearby vehicles and
other objects.
Radar detects
both moving and stationary objects by measuring the reflected energy off of
them.
Lasers are able
to measure the distance between objects very accurately and quickly
All of these sensors work together to create a detailed
picture of the environment so that the ADAS system can make informed decisions
about the best way to operate the vehicle.
By utilizing these sensors, ADAS is able to detect potential
hazards on the road and alert drivers in order to prevent an accident. This
makes it easier for drivers to stay safe on the road and reduce their chances
of being involved in a crash. So, it’s important to make sure that your ADAS
system is working properly in order to get the most out of it.
.gif)


.jpeg)
