A Reciprocating engine is a type of engine that uses pistons to convert pressure into mechanical work.
Reciprocating Engine
 |
| Engine |
 |
| Engine |
A Reciprocating engine is a type of engine that uses pistons to convert pressure into mechanical work. It is also known as a piston engine and is commonly found in automobiles, trucks, ships, locomotives, and various other machinery. This type of engine has been used since the late 19th century and has seen many advances in technology over the years. Reciprocating engines have many advantages, including their ability to provide power for a wide variety of applications, and their relatively low cost compared to other types of engines.
What is a Reciprocating engine?
Reciprocating engines work by taking air and fuel and mixing them together inside of a combustion chamber. This mixture is then ignited with a spark plug and this creates a rapid expansion of the gases inside the chamber. The result of this expansion is an increase in pressure which pushes against the walls of the cylinder and forces the piston downwards. This downward force is transferred to a crankshaft which then converts the linear motion into rotational motion. This rotational motion can then be used to power various types of machinery.
How does a Reciprocating engine work?
A reciprocating engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses pistons to convert pressure into mechanical work. The pistons move up and down in cylinders, which are hollow tubes inside the engine. As the piston moves up and down, it compresses and expands the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinder, creating a combustion event.
The power for the piston movement comes from the pressure created when the fuel and air inside the cylinder combusts. This pressure forces the piston downwards, turning the crankshaft, which is connected to the pistons by connecting rods. This motion creates the rotary motion necessary for powering a vehicle.
The cycle begins again when the piston returns to its initial position at the top of the cylinder. A valve opens, allowing fresh air and fuel to enter the cylinder, while exhaust is released through another valve. The cycle repeats itself continuously, creating rotational energy to power the vehicle.
Reciprocating engines are used in a wide range of applications, including cars, trucks, airplanes, boats, and generators. They are relatively simple to operate and maintain and are known for their reliability and efficiency.
 |
| Engine inner View |
What are the benefits of using a Reciprocating engine?
Reciprocating engines are a popular choice for power generation due to their reliability and efficiency. They are able to convert pressure into mechanical work quickly and efficiently, allowing for more efficient operation of the engine. The design of a reciprocating engine is also relatively simple, allowing for easy maintenance and servicing. Additionally, the size of a reciprocating engine makes it ideal for many applications, from large industrial machines to small portable generators.
Another benefit of using a reciprocating engine is that they are often less expensive to maintain than other types of engines. Because of their simple design and lack of moving parts, they can often be maintained with minimal parts replacement and labor costs. In addition, their durability and longevity make them a great choice for long-term applications where costs savings are important.
Finally, reciprocating engines are generally easier to control than other types of engines. They can be used to provide steady and reliable power output and can easily be adjusted to meet changing load requirements. This makes them well suited for many different applications.
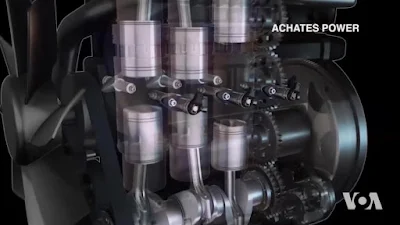 |
| Reciprocating Engine |
What are some drawbacks of Reciprocating engines?
Reciprocating engines have a number of drawbacks that need to be considered when selecting the best power source for a particular application. One major drawback of reciprocating engines is their relatively low efficiency compared to other types of engines. Reciprocating engines also require more maintenance due to their complex design and moving parts. Additionally, they tend to produce higher levels of pollutants than other engines and are often noisy. As such, care must be taken when locating reciprocating engines near residential areas or sensitive ecosystems. Lastly, reciprocating engines are typically larger and heavier than other types of engines, making them more difficult to transport and install.
What is Reciprocating engine system?
A reciprocating engine system is an arrangement of components used to produce mechanical energy through the use of a piston. The basic components of a reciprocating engine system include a cylinder, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, and valves.
The cylinder is where combustion occurs. It is the space in which the piston moves up and down within the chamber. The piston is connected to the crankshaft via a connecting rod, which converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. The crankshaft is then connected to a drive shaft, which transmits power to other components. Valves are also included in the system, allowing for the introduction of fuel and air during combustion and for the expulsion of exhaust gases.
The mechanical energy generated by the reciprocating engine system is used in many applications, from powering automobiles to running machinery. The system is relatively simple and reliable, making it a popular choice for many industries. However, reciprocating engines can be inefficient when compared to other types of engine systems, such as turbos or electric motors. Additionally, they are noisy and require frequent maintenance to ensure optimum performance.
What are the 4 types of Reciprocating engines?
1. Four-stroke engines: A four-stroke engine, also known as a "four-cycle" engine, works by first compressing a mixture of air and fuel, then igniting it to create power. This cycle occurs four times per power stroke in order to produce the desired power output.
2. Two-stroke engines: A two-stroke engine is similar to a four-stroke engine but differs in that it only needs two strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle. This type of engine is often found in small engines such as those used in lawn mowers and other handheld tools.
3. Opposed-piston engines: An opposed-piston engine works by having two opposing pistons connected to a common crank shaft. This type of engine is usually found in aircraft or marine applications and is characterized by its low vibration and noise output.
4. Rotary engines: Rotary engines are an old technology that was popularized by the German company Wankel AG in the 1950s. This type of engine is characterized by its use of triangular rotors that spin inside of an oval-shaped combustion chamber to produce power. The rotors also help to reduce vibration and noise levels, making it suitable for use in automobiles.

.jpeg)

