The Transmission: How Power is Transferred from an Engine to an Axle in a Motor Vehicle
Transmission
Transmission is the most important components of a motor vehicle, as it is the mechanism by which power is transferred from the engine to the axle. Without transmission, the engine's power not able to propel the vehicle forward. Understanding the basics transmission works to help you make decisions about maintaining your vehicle and keeping it in optimal condition. In this blog post, we will explore the inner workings of the transmission and how it transfers power from the engine to the axle in a motor vehicle.
What is a Transmission?
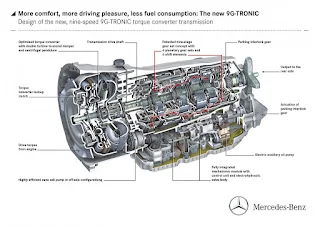 |
| Transmission Parts |
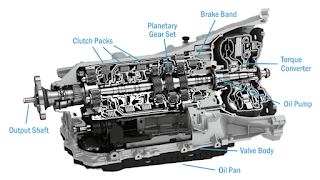 |
| Transmission |
A transmission is the mechanical device that transfers power from an engine to the drive axle in a motor vehicle. The transmission converts the rotational force of the engine into motion, allowing the car to move forward or backward as desired. It also allows the driver to control the speed of the car and the amount of power it uses when accelerating or decelerating. The transmission is responsible for shifting the gears, which determines how much torque is available for acceleration. In manual transmissions, the driver must shift gears manually, while automatic transmissions use a computer-controlled system to select the proper gear at any given moment.
Types of Transmissions
When it comes to transmission systems, there are several different types of transmissions used in motor vehicles. The most common are manual and automatic transmissions, but there are also other types such as continuously variable transmissions (CVT), dual-clutch transmissions (DCT), and semi-automatic transmissions.
Manual transmissions are the most basic type and use a clutch to disengage the engine from the axle, allowing for smooth shifting between gears. The driver must manually operate the clutch pedal and shift lever to change gears.
Automatic transmissions are the most common type used today and use planetary gears to create smooth shifts without the need for a clutch pedal or shift lever. The transmission is controlled by electronic control unit (ECU) that determines when to shift.
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) are a type of transmission that uses a belt and pulley system to create an infinite range of gear ratios. This allows the vehicle to maintain a constant speed with minimal driver input.
Dual-clutch Transmissions (DCT) are similar to manual transmissions in that they use two separate clutches to engage and disengage the engine from the axle. However, the difference is that they allow for quicker shifts since both clutches can be engaged at the same time.
Finally, semi-automatic transmissions are a hybrid of manual and automatic transmissions. They use an electronically controlled clutch to disengage the engine from the axle, but the driver must still manually select the gears using a shift lever.
The Function of a Transmission
The transmission is the component in a motor vehicle that transfers the power generated by the engine to the axle, which drives the vehicle forward. It is responsible for controlling the speed and torque of the vehicle and for providing efficient operation. The transmission is also responsible for controlling how much fuel is consumed by the engine and for providing smooth shifting between gears.
When an engine is running, it produces torque and power that must be transferred to the wheels in order to drive the vehicle. The transmission is the link between the engine and the axle, allowing them to work together and allowing the driver to control the speed and power output of the vehicle.
In manual transmissions, the driver controls the speed and torque of the engine with a clutch and a gear shift lever. The clutch allows the driver to disengage the engine from the transmission so that they can change gears without stopping the vehicle. The gear shift lever is used to select a specific gear ratio for a given speed or torque output.
In automatic transmissions, a torque converter is used to transfer power from the engine to the transmission, and then from the transmission to the axle. The torque converter uses hydraulic pressure to convert rotational energy from the engine into mechanical energy that can be used to drive the vehicle. The transmission then uses a set of gears, called a planetary gearset, to change the torque and speed of the vehicle.
The function of a transmission is critical to a motor vehicle’s operation. It allows an engine to produce the maximum amount of power and torque without damaging the engine or axle, and provides smooth operation for both manual and automatic transmissions. By controlling the amount of fuel consumed by an engine and ensuring smooth shifting between gears, a transmission ensures efficient operation of a motor vehicle.
How Power is Transferred from an Engine to an Axle in a Motor Vehicle
The transmission is an essential part of a motor vehicle, as it is the mechanism by which power from the engine is transferred to the axle. This power transfer is accomplished through the use of gears, shafts, and other components.
The transmission works by first transferring the power from the engine to a set of gears. These gears are connected to a shaft, which is connected to the axle of the vehicle. The shaft then turns the axle, which powers the wheels and allows the vehicle to move.
The type of transmission that is used depends on the size and power of the engine and the purpose of the vehicle. Generally, most cars use either manual or automatic transmissions. Manual transmissions require the driver to manually shift gears in order to change speed. Automatic transmissions are self-shifting and will automatically adjust the gear ratio in order to match the speed of the car.
The transmission works by connecting different sized gears in order to match the speed of the engine to that of the axle. The gears are connected by a series of shafts and other components, which allow them to turn and transfer power between them. The size of the gears determines the speed at which they can transfer power, so larger gears are used for higher speeds and smaller gears are used for slower speeds.
In order to ensure that the transmission is able to handle high levels of power and torque, it must be constructed out of materials that can withstand such forces. Common materials used for transmissions include steel and aluminum alloys, although other materials such as carbon fiber and composites are also used in some cases.
In conclusion, transmissions are a vital component of any motor vehicle, as they enable power to be transferred from the engine to the axle in order to move the vehicle. By using different sized gears and other components, the transmission is able to adjust the gear ratio so that it matches the speed of the engine and axle, allowing for efficient power transfer.


.jpeg)
